INTRODUCTION
Google Ads was founded barely two years after Google.com, the world’s most popular website. The advertising platform first appeared in October 2000 as Google Adwords; however, it was renamed Google Ads in 2018 following the significant rebranding.
Given Google’s extensive reach, you’ve undoubtedly seen (and presumably clicked on) a Google ad… and so have your potential consumers. This post will teach you how to start advertising on Google.
GOOGLE ADS AND THEIR BASICS
Google Ads is an advertising platform that comes within the pay-per-click (PPC) marketing channel, in which you pay per click or impression (CPM) on an ad.
Google Ads is an efficient approach to deliver qualified visitors, or good-fit clients, to your business when searching for items and services like the ones you provide. You can enhance your website traffic, phone calls, and in-store visits by using Google Ads.
Google Adverts enables you to design and distribute well-timed ads to your target audience (through mobile and desktop). This implies that your company will appear on the search engine results page (SERP) when your ideal consumers search for items and services like yours on Google Search or Google Maps. In this manner, you reach your target audience at the optimal time for them to see your ad.
Google is one of the most popular search engines, with over 5 billion searches every day. Google Ads platform has been in operation for over two decades, giving it significant clout in the paid advertising space. Furthermore, according to Google, advertisers earn $8 for every $1 spent on Google Ads.
The highest bidder receives the prize in most auctions, and everyone else is evicted. The bids in Google Ads are usually hidden, and the highest bidder does not necessarily obtain the top slot. Other considerations, such as quality score, decide which advertising wins. If your quality score for a specific term is good enough, Google may not even charge you the whole amount of your maximum bid.
PPC AND NETWORKING
Google Advertising is the most popular ad network owing to the enormous number of websites on the Google Display Network and the accessible reach of ads in the number of queries done in the Google search engine (GDN).
“Google Advertisements display ads appear on over two million websites and in over 650,000 applications, so your ad may appear everywhere your audience is,” Google says. Remarketing, in-market audiences, comparable audiences, and other targeting options are available on the display network.
Age, gender, parenting status, and family income may be targeted in search and display advertisements. Including demographic targeting reduces the possible reach for advertising while making the targeting more relevant.
Google search engine results, GDN online placements, retail, mobile applications, and YouTube are all examples of placements. Text, picture, responsive, and video ads are available.
Pricing is determined by a cost-per-click (CPC) mechanism depending on competition and ad quality. GDN provides for a cost-per-1,000-impressions model (CPM).
Tip: Depending on the business, advertisers will discover greater CPCs for search phrases on Google Ads. It’s time to be inventive, try a highly relevant display network campaign, or go to another platform.
Using a planner helps you keep track of your PPC efforts. You can visualize how your advertisements will appear online, monitor your character counts, and manage your campaigns all in one location using Google and HubSpot’s PPC Planning Template.
TYPES OF ADS

Standard Text Ads (ETAs)
Text advertising used to be relatively simple, with a tight character restriction and little space for creativity in wording or including top keywords for improved ranks. Google extended these advertising a few years ago into what is now known as expanded text ads (ETAs). ETAs allow for up to three headlines and two descriptions, as well as “extensions” that allow you to include things like phone numbers and links to various sections of your website. ETAs are a tried-and-true sponsored search approach that all advertisers should consider.
Responsive Search Ads (RSAs)
RSAs are like ETAs on steroids. They provide additional alternatives for headlines (14) and descriptions (5), allowing for larger reach and A/B testing without the need for separate advertisements. Google will test various combinations of your headlines and descriptions until it finds the most successful combination for reaching potential buyers with the most engaging text at the appropriate moment.
Dynamic Search Ads (DSAs)
Dynamic search advertising is an automated ad kind that dynamically populates search advertisements with material from your website. These advertisements are intended to be used with well-developed websites with distinct content categories and a significant inventory of items. DSAs target your advertising to customers seeking comparable items or services based on the content on your website. This saves you time during setup and guarantees you’re utilizing keywords you could have missed otherwise. However, you have little influence over what your ad will say because of the automation.
Image Ads
Image advertisements run on the Google Display Network, which means they can appear on websites partnered with Google to supply ad space; Google will pick to display them on websites that your main audience visits regularly. Image ads, also known as display ads, can be stationary or interactive visuals and are best suited for brand recognition campaigns. In contrast, text ads are more suited for people farther down the marketing funnel.
Video Ads
Several video ad types enable you to provide a more engaging experience while targeting clients on Google Partner platforms such as YouTube. Video advertising is a profitable ad type with a high ROI, and it is highly recommended for businesses with the means to invest in video assets. Fun facts: Over 500 million hours of video material are seen on YouTube alone in a single day, and video consumption accounts for one-third of all internet activity.
Product Shopping Ads
Product shopping advertisements display things for sale together with a product image, title, price, and store link. All this data is retrieved from your Google Merchant Centre account via the product feed you supply. Your product shopping ad campaign will appear on Google Shopping, Images, and search partner websites — also at the top of the search engine results page (SERP).
Showcase Shopping Ads
Showcase shopping ads are distinct from product shopping advertisements in that they gather a certain range of items together, allowing you to market a wide range of products. These ads appear less frequently than product shopping advertisements, but they allow viewers to browse goods before clicking and have a wider reach because they are shown to people searching for more broad terms, such as “phone cases.”
Call-Only Ads
Call-only advertising is displayed on mobile devices and enables you to promote phone calls. These can be configured to always operate exclusively during business hours or. When a person clicks on the ad, it calls you immediately from the SERP. These ads will still have headlines and descriptions and seem like ordinary text advertising. However, unlike call extensions, these ad kinds run as their ad, inviting a user to call your business directly, whereas text advertisements take the visitor to a landing page.
MECHANISM BEHIND GOOGLE ADS
Google’s advertising mechanism is like an auction with a few exceptions. As an advertiser, you select the search keywords you want your ad to appear and establish a maximum bid for how much you’re ready to pay when someone clicks on your ad. This is when the phrase “cost per click” (CPC) comes into play.
The quantity of that bid (in comparison to other bidders on the same phrase) will help Google evaluate where your ad will appear on the page.
The highest bidder receives the prize in most auctions, and everyone else is evicted. The bids in Google Ads are usually hidden, and the highest bidder does not necessarily obtain the top slot. Other considerations, such as quality score, decide which advertising wins. If your quality score for a specific term is good enough, Google may not even charge you the whole amount of your maximum bid.
Your quality score is based on how effectively your landing page matches the search phrase you’re bidding on, as well as how well you can deliver on what the visitor was looking for. The more relevant your ad and landing page are to the search, the less you will have to spend for the ad and acquire the click.
It may appear that you must account for thousands of search variables to get a high ad position and click. You do, in a sense, but there are simple tactics in Google Ads that make it simple and practical automated. For example, match kinds and ad groups can help you segregate your messages to more closely align with the user’s purpose.
CAMPAIGN SETTINGS
The campaign parameters you choose will be applied to all advertisements in the same campaign. The parameters accessible to you are determined by the sort of campaign you select.
Several Google Ads campaign options are available and conflicting recommendations on how to configure them.
Incorrect settings will hinder your results regardless of the high intent keywords you chose or the superior advertising you produce.
You can get in a lot of trouble if your settings aren’t right.
Do Not Allow Google to Manage Your Google Ads Campaigns
Google reportedly emailed advertisers with the subject line, “We’ll focus on your campaigns so you can focus on your business.” Doesn’t it sound nice? Consider it again. Google is bringing in “Google Ads professionals” to manage marketers’ campaigns, with the caveat that doing so “doesn’t guarantee or promise any specific results from applying these improvements.” Unless you click the opt-out link in the email, this happens automatically. Google’s default management may not be the greatest option for your brand because Google does not know your individual goals or create income for your company.
Determine whether your ad campaign makes more sense in search or display.
When creating a Google Ads campaign, you’ll first decide whether to run a Search or Display campaign. By default, when you select Search, Google selects the option that reads “Include Google Display Network.” Make certain that this is not chosen! Because the aims of each are different, search marketing should always be kept distinct from display advertisements. The Display network is designed particularly for image or video advertisements. When text advertisements are broadcast on the Display Network, they are often disregarded, resulting in fewer quality clicks, and wasted ad spend—not ideal for generating conversions. Keep your Search and Display advertising distinct for the greatest results.
Bidding Methods: Automated vs. Manual
When creating a Google Ad Campaign, you’ll make one of the first decisions is using the bidding method. You may choose between an automatic bid plan, maximizing conversions, and a manual CPC (cost-per-click) approach. If you’re planning to pause and resume your Google Ad campaign for whatever reason, use the manual CPC option.
What is the significance of this? If you choose an automatic bidding approach, Google’s machine learning starts over every time you restart your campaign. Any previously collected data is no longer used, and conversion optimizations are lost. Furthermore, automatic bidding techniques will regard all your conversions as equal unless you change the parameters if you have many conversions with no dollar values specified.
Choose Keyword Match Types That Are Appropriate for Your Google Ads Campaign
When you start a Google Advertisements campaign and enter your keywords, you can choose which keyword match types will activate your ads when they are searched for. Keyword matches are classified into four types: wide, modified broad, phrase, and precise. There are other keyword match kinds for negative keywords or phrases that you do not want your advertisements to appear for. Blue Compass employs several match types to capture the queries we wish to appear.
We often advise against wide-match keywords since they are too broad. Instead, we build a modified wide, exact match, and phrase match keyword for each of our top inquiries. Do you know what each match type means? We’ve defined the various match types and provided examples of using each keyword match type below.
ACCOUNT OPTIMIZATION
The optimization score is based on how effectively your account is configured to perform across Search, Display, and Shopping. It generates customized account-specific recommendations based on the following criteria:
- Extensions and advertisements
- Automated campaigns
- Budgets and Bidding
- Repairs
- Keywords and Targeting
At first, Google Ads optimization might seem frightening, but it doesn’t have to be. Optimizing a Google account is considerably simpler than you would assume. All it takes is some research and strategy and adherence to some well-established PPC best practices.
FOCAL POINTS IN GOOGLE ADS
A focal point is a point of interest, focus, or emphasis in a design intended to draw the user’s attention. These main points must stand out from the rest of the design elements. As an example of a focus point, consider the following:
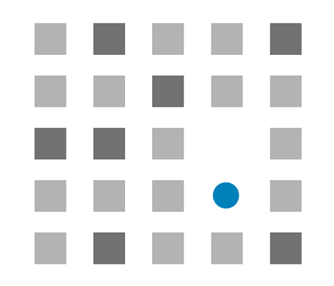
The blue circle is the main point since it is distinctive and immediately draws attention. Although not as obvious as the blue circle, the dark-colored squares are focus points. You may have numerous focal points in a design that lead the user’s visual attention to the primary focal point.
The focal point design technique directs viewers to places of interest where you want them to perform a particular action (usually conversion).
Keyword positioning
Keywords should be deliberately inserted throughout the material to indicate what topics will cover search engines and users. This implies that keywords should appear organically throughout the material and in the headers and tags, title, meta tags, and meta description.
Keyword research is the process of locating the best keywords for your article. You do keyword research by looking at the search patterns for various phrases, which allows you to discover which concepts and ideas have gotten a lot of attention and which haven’t. This will inform you where the customer’s emphasis is to generate content to meet their wants.
Cater to the user’s query
According to research, our eyes move 4–5 times each second while we read or watch a static scene.
To be successful, your page must strike a balance. You can’t overemphasize everything and hope for the best. It is critical to establish dominance on the page and create focal points to attract the greatest attention. If the purpose of your page is to create the most conversions, your average user will immediately go for the CTA button and other clickables. You may take advantage of this by dominating the page with a call-to-action button. You can have the most important knowledge at the second degree of domination. For instance, what should your user expect after clicking the link? Finally, you can leave a white space or generic body text at the bottom of the hierarchy.
Mandatory call to action
The call-to-action, or CTA, is a constant element that connects these touch-points. CTAs are more than just a logistical UX element; they also provide an opportunity to persuade and create trust. But how can you develop appealing calls to action that your prospects, customers, and users won’t be able to ignore?
PPC Call-to-Action Examples
Countsy
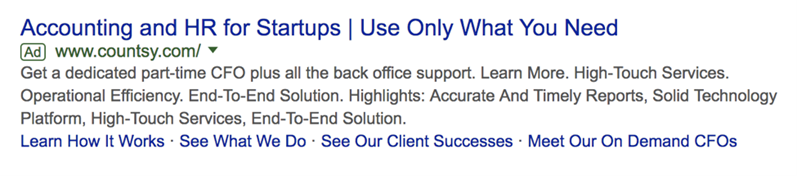
Camtasia
Lightroom

Creating the ideal call-to-action might feel like an exact science. Hopefully, some of these CTA examples have influenced you!
Use relevant ad extensions and features.
Extensions provide extra information to your ad, giving customers more reasons to pick your company. These can enhance the clickthrough rate of an ad by several percentage points. Examples of extension formats include call buttons, geographical information, connections to specific portions of your website, additional content, and other forms.
Google Advertising chooses which extensions to show in response to each Google search to enhance the success of your text ads. As a result, it’s a good idea to employ all the extensions that are important to your company goals.
Extensions increase the visibility of your ad on the search results page by adding extra content to it. This means you’ll receive more bang for your buck from your ad. Extensions frequently enhance your overall number of clicks and can provide visitors with more interactive ways to contact you, such as maps or phone calls.
There are two kinds of extensions: manual extensions and automatic extensions. Manual extensions take some configuration, but automated extensions are applied automatically when Google Ads estimates that they increase your ad performance. Because automated extensions do not require any setup, they will not appear as alternatives when establishing manual extensions.
CONNECTING WITH THE AUDIENCE
Currently, the following audiences are available:
- Visitors to your website are those who come to your site and reach a page, reach one page but not another, or do another particular action.
- People that have subscribed to your channel viewed a video/ad or commented/liked a video are examples of YouTube audiences.
- People who have proved that they are actively seeking the product/service you offer are considered in-market.
- Affinity: Groupings of general interests based on sites visited and searches completed.
- Custom affinity/intent: Focuses on interests or purchasing intent using keywords/URLs.
- Life events: Best estimations based on searches and sites visited on significant anniversaries.
- Detailed demographics: Information provided voluntarily (age/income/gender/home ownership/parent).
- Customer Lists: Email addresses and location data obtained with the permission of your customers/prospects.
- Similar Audiences: People who appear to share characteristics with existing audiences.
Determine prospective/remarketing audience
Remarketing allows you to keep your adverts in front of individuals who have previously visited your website or app. Consumers visit mobile websites an average of six times during the purchasing process. When they’re most inclined to buy, you should re-engage them.
If you have a wide product portfolio (retail or travel), you should start with dynamic remarketing. This will display potential buyers the most relevant ad based on your existing inventory, avoiding the need to create hundreds of advertisings.
Because we’re talking about AdWords remarketing, there are several methods you might reach your target demographic via a display ad.
You can utilize the platforms/networks listed below —
- YouTube
- Gmail
- Apps
- Display Network
- Remarketing Search Listings Ads
There are three types of remarketing campaigns that you could wish to perform in general.
- Campaigns focused on users who did not complete a certain action on a website — for example, generating leads from those who did not opt-in on your landing pages.
- Campaigns focused on customers who reached a given point in your checkout process but did not finish their purchase– for example, converting cart abandoners.
- Campaigns for visitors who haven’t visited a page you’d like them to visit.
- After seeing your remarketing campaign, you must know exactly what action you want your potential consumer to take.
Once you’ve determined that, you may proceed with the next steps:
- Choosing which pages should have remarketing tags.
- Choosing a network and determining how to reach out to your target demographic on that network.
- Understanding how to produce advertisements that are suited to your target demographic.
- Creating personalized pages for the audiences, you’re remarketing to.
- Knowing how to handle each of these factors is critical to obtain the best outcomes from your remarketing efforts.
Usage of triggers
A few of the most important reasons for using click triggers are as follows:
- On a mobile page, the user clicks on a phone number.
- To find directions from Google Maps, click here.
- Clicks on a link that takes you to a new domain.
- Clicks to submit a form but do not result in a redirect
This is by no means an exhaustive list. There are many circumstances in which you would like to use click triggers instead of or in addition to URL page visits. Whatever the cause, designing and troubleshooting click triggers are relatively similar.
When shooting tags through GTM, click triggers work the same way as any trigger. Once a click trigger is established, it may be applied to any new or existing tag with no changes to the tag parameters necessary.
In GTM, click triggers are not platform-specific. If the same trigger is used for multiple tags, a single trigger may be used to fire them across various platforms and does not need to be duplicated.
Maintain quality score (QS)
Quality Score is a diagnostic tool that will tell you how well your ad quality compares to other marketers. This score, which ranges from 1 to 10, is provided at the keyword level. A higher Quality Score indicates that, when compared to other marketers, your ad and landing page are more relevant and beneficial to someone looking for your term.
You may use the Quality Score diagnostic tool to see where you can enhance your advertisements, landing pages, or keyword choices. The Quality Score is produced by combining the performance of three components:
- Expected clickthrough rate (CTR): The probability that your ad will be clicked when displayed.
- Ad relevance: The degree to which your ad fits the intent behind a user’s search.
- Landing page experience: The relevance and usefulness of your landing page to those who click on your ad.
Each element is rated as “Above average,” “Average,” or “Below average.” This assessment compares other marketers whose advertisements appeared for the same keyword within 90 days. If one of these elements has a status of “Average” or “Below Average,” this may suggest a chance to improve.
Because Quality Score is calculated based on historical impressions for precise searches of your phrase, altering keyword match types does not affect Quality Score. If you see “—” in the Quality Score column, it implies there aren’t enough searches that exactly match your keywords to estimate the Quality Score of that phrase.
There are several aspects of ad quality that Quality Score may not represent. Among these criteria include, but are not limited to:
- Devices used in search
- Location of user
- Time of day
- Ad extensions
STRATEGIES AND KEY TERMS
You must know exactly what you want to aim with your campaign. Is there a set number of leads every month? Do you want your website to generate phone calls, newsletter signups, or sales? Is there a certain cost per conversion that you’d want to achieve?
Understand your objectives first since they will influence how you set up and run your campaign. When working on a new campaign, here is where you will spend most of your time. Here are the three sorts of research to conduct:
- Keyword Research: Use keyword tools to discover the most relevant terms that people search engines to locate your product/service/company. Plan to spend at least a few hours on this…it will serve as the foundation of your campaign.
- Competitive research entails investigating the firms bidding on these keywords in AdWords. Look at who consistently ranks near or at the top of the rankings (you can use a spy tool like iSpionage to help). Please take note of their ad wording and offers. Go to their websites. Subscribe to their mailing lists. Purchase their goods.
- Investigate Your Audience: Where are people buying and evaluating similar products/services/businesses online? Examine their feedback. What do they like or dislike about your competition? What are the deep needs/desires they want to fulfill? What emotions are they displaying? Look for great quotations to utilize as ad text when investigating them.
Metrics and features
The following are the most important Google Ads metrics, as determined by the paid search metrics that our clients most often track in Databox.
- Overview of the campaign. Which commercials get the most attention? Get total visibility into your ongoing Google Ads campaigns and track their effectiveness in real-time.
- View the total no. of times your ad was seen on Google or the Google Network every day, week, month, year, or within the selected calendar range.
- Visually track the number of clicks your ad receives each day. It aids in tracking this data because it is a good sign that your ad is captivating and helpful to those who see it.
- How much do I pay for each ad click? See how much you pay on average for each click on your ad.
- How many users took the necessary action after clicking on my advertisements? Determine if your ad clicks are resulting in the necessary action being taken by users.
- Price per Conversion (CPC). How much does conversion on my advertising cost on average? See how much you’re charged for each desired action a user takes after seeing your ad.
Automates rules
Automated rules allow you to automatically change your account, depending on the settings and criteria that you specify. You may modify your ad status, budget, bids, and other settings. You may, for example, implement a rule to increase your keyword bid if your ad slips off the first page of results. Furthermore, you may utilize automated rules to send emails without further action when certain circumstances are met.
Using automatic rules can save you time by reducing the need to monitor campaigns and make manual modifications regularly.
Bidding strategies
Google Ads provides several bid strategies geared to various sorts of campaigns. Which strategy is optimal for you depends on which networks your campaign is targeting and if you want to focus on gaining clicks, impressions, conversions, or views? In this post, we’ll go through how to determine your bid strategy based on your advertising goals.
Each bid technique is best suited for specific campaigns and advertising goals. You’ll want to consider five main sorts of goals, as well as your current campaign parameters while bidding. If you wish the customers to take direct action on your site and measure conversions, it could be ideal for focusing on conversions. Smart Bidding enables you to do so.
If you wish to drive traffic to your website, concentrating on clicks may be the way to go. CPC bidding may be appropriate for your campaign. Focusing on impressions may be a good method to boost brand recognition. You may employ cost-per-thousand viewable impressions (CPM) Bidding to get your message in front of customers.
If you want to enhance the number of views or interactions with your video advertising, you may utilize cost-per-view (CPV) or cost-per-thousand-impressions (CPM) bidding.
Five Smart Bidding strategies you can use
- Target cost per action (CPA): If you wish to optimize for conversions, you may utilize Target CPA to boost conversions while focusing on a specified cost per action.
- Return on ad spend (ROAS): If your wish is to optimize for conversion value, Target ROAS can assist you in boosting conversion value while targeting a specified return on ad spend (ROAS).
- Maximize Conversions: Use Maximize Conversions to optimize for conversions but don’t spend your entire budget on a certain CPA.
- Maximize Conversion Value: If you wish to optimize for conversion value but don’t want to spend your entire budget, you may utilize Maximize Conversion Value. Learn more about Bidding to Maximize Conversion Value.
- Enhanced cost per click (ECPC): Use ECPC to alter your manual bids to increase conversions automatically. It is an optional feature that may be used with Manual CPC bidding. Find out more about the ECPC.
Focus on clicks
- Maximize Clicks: This is an automated bid approach. It’s the most basic technique to bid on clicks. Pick an average daily budget, and the Google Ads system will automatically manage your bids to offer you the most clicks possible within your budget.
- Manual CPC bidding allows you to set your own maximum CPC bids. Different bids may be specified for each ad group in your campaign, as well as for specific keywords or placements. If you’ve discovered that keywords or places are more successful, you may use manual Bidding to direct a larger portion of your advertising budget toward those keywords or spots.
Focus on visibility
- Target Impression Share: establishes bids to display your ad at the absolute top of the page, at the top of the page, or anyplace on the page of Google search results. More information on Target Impression Share may be found here.
- CPM: With this bidding approach, you’ll pay depending on the number of impressions (the number of times your advertisements appear on YouTube or the Google Display Network).
- tCPM: A bidding approach where you establish an average for how much you’re prepared to spend per thousand impressions. It optimizes bids to enhance the unique reach of your campaign. You can use tCPM to maintain your campaign’s average CPM below or equal to the target you specify (although the cost of impressions may vary).
- vCPM: This is a manual bidding approach that you might do if your advertising is intended to raise awareness but not necessarily drive clicks or traffic. It allows you to choose the maximum amount you wish to spend per 1,000 visible ad impressions on the Google Display Network.
Setting a CPA
Target CPA bidding is a Smart Bidding approach that sets bids to maximize conversions (customer actions). When you design the Target CPA (target cost-per-action) bid strategy, you provide an average cost for each conversion. When a consumer performs a Google search for your product or service, Google Ads sets a bid based on the auction’s likelihood to convert using your Target CPA.
Target CPA bidding sets an appropriate bid for your ad each time it is eligible to appear by using past data about your campaign and contextual signals present at auction time.
Some conversions might cost more than your target, while others may cost less, but Google Ads will make every effort to maintain your cost per conversion like the target CPA you set. These CPA variations occur because your real CPA is affected by variables outside Google’s control, such as changes to your website or advertisements or greater competition in ad auctions. Furthermore, your actual conversion rate may be lower or greater than your expected conversion rate.
CONVERSION SETTINGS AND ATTRIBUTION MODELS
Conversion Settings
You might have to choose to include each conversion goal by default across all campaigns in your account for each conversion objective. Suppose you enable the “account default” setting for a conversion goal. In that case, the key conversion actions within that goal will be monitored as conversions in your reports and utilized for bidding across all your campaigns (save those where campaign-specific goals have been set up).
Instructions
- Go to your Google Ads account and sign in.
- Click on the Tools button in the upper right corner and click Conversions under “Measurement.”
- Select the conversion action you wish to modify by clicking its name.
- Click the Edit settings button.
- Include in “Conversions” by clicking Include in “Conversions”…
- Click Save, followed by Done.
Attribution Models
Customers may interact with many adverts from the same advertiser on the road to conversion. You may specify how much credit each ad interaction receives for your conversions using attribution models. Attribution models may help you optimize conversion pathways by providing a deeper knowledge of how your advertising works.
Most advertisers assess the performance of their internet advertising based on the “final click.” This means that they attribute the whole conversion to the last-clicked ad and matching keyword. This, however, overlooks any previous ad encounters that clients may have had along the route.
Attribution models allow you greater say over how much credit each ad interaction receives for conversions. This enables you to:
- Reach clients early in the buying cycle: Look for ways to impact clients earlier in the conversion process.
- Match your company: Use a model that best fits consumers’ look for what you have to offer.
- Increase your Bidding: Improve your bids based on a deeper knowledge of how your advertising is doing.
Google Ads provides the following attribution models:
- The most recent click Last click: Assigns full credit for converting the most recently clicked ad and matching keyword. First, click here. Initially click: Assigns sole responsibility for converting the ad and keyword that was clicked first.
- Linear: Distributes conversion credit evenly across all ad interactions on the journey.
- Time decay: The passage of time gives extra weight to ad interactions near the conversion. A 7-day half-life is used to award credit. In other words, an ad engagement eight days before a conversion is worth half as much as an ad interaction one day before a conversion.
- Position-based: Allocates 40% of the credit to the first and final ad interactions and relevant keywords, with the remaining 20% distributed throughout the other ad interactions on the path.
- Data-driven: Credit for the conversion is distributed depending on your previous data for this conversion operation. It differs from the previous models in that it calculates the real contribution of each interaction along the conversion path using data from your account. Find out more about data-driven attribution.
CREATE YOUR OWN GOOGLE AD!
Link analytics account to google ads
By connecting your Google Advertisements account to your Analytics property, you can observe the whole customer journey, from how customers interact with your marketing (e.g., seeing ad impressions, clicking ads) to how they achieve the goals you’ve established for them on your site (e.g., making purchases, consuming content).
When you connect Google Ads and Analytics, you may do the following:
- In the Google Ads reports in Analytics, you can view ad and site performance statistics.
- Import Analytics objectives and transactions into your Google Ads account.
- When you enable Google signals, you may import cross-device conversions into your Google Ads account.
- Import Analytics analytics into your Google Ads accounts, such as Bounce Rate, Average Session Duration, and Pages/Session.
- Analytics Remarketing and Dynamic Remarketing can help you improve your Google Ads remarketing.
- Richer data is available in the Analytics Multi-Channel Funnels reports.
A maximum of 400 link groups can be assigned to each Analytics attribute. A maximum of 1,000 Google Ads accounts can be assigned to each link group. When Google Ads (MCC or individual account) is disabled/canceled, you cannot link Analytics and Google Ads.
UTM codes to track
A UTM code is a basic block of code that may be added to the end of a URL to track the performance of campaigns and content. You may track URL parameters in five ways: source, medium, campaign, term, and content. Dimensions tracked using UTM codes appear in analytics reports, providing a clearer picture of marketing effectiveness.
The UTM code is made up of two parts:
- UTM Parameter – begins with UTM. You may track five different parameters: utmsource, UTM campaign, UTM content, and UTM term (more on these below).
- Tracking variable — a one-of-a-kind variable that identifies the dimension being tracked (such as the name of the traffic source). The “=” symbol precedes this variable. The variable can include integers, characters, hyphens, the ‘+’ symbol, and periods.
Track conversion
When you run Google Advertisements ads, you may want to know if clicks on your ad lead to a particular action, such as a purchase on your website, a phone call, or an app download. The first step in conversion monitoring is deciding what you want to track.
Conversion tracking is a useful feature in Google Ads that allows you to determine how successfully your ad campaign produces leads, purchases, downloads, email signups, and other important business activities. Conversion monitoring data helps you see which aspects of your campaign are working and which are not, allowing you to tweak your bids, ad content, and keywords accordingly.
To begin, go to Google Ads’ Tools and Analysis tab and pick Conversions from the drop-down menu, which takes you to the All-conversions page. Go to the Conversions tab and click the +Conversion button to make your first conversion.
Combine Google ads and CRM
CRM for Google Ads provides a comprehensive view of the money generated by your online ad campaigns. You’ll be able to track your ad expenditure inside CRM from your customer’s initial click until your rep closes the sale, allowing you to understand which campaigns are working and which aren’t.
Concentrate on the appropriate terms.
CRM integrates sales data with Google Ads expenditure to determine which phrases generate the most qualified leads. Spend your advertising money where they will have the greatest impact, and you will receive a greater return on your investment if you target your best leads. You can persuade a prospect with a stronger sales pitch if you know why they came to your website. Salespeople can see which advertising consumers clicked on and keywords they used to locate your company in CRM. You can make every pitch more relevant by reviewing campaign data in your client records.
Fill the void between internet conversions and offline purchases.
Agencies or internet marketers in charge of Google Ads for your organization no longer need to be in the dark regarding sales conversions. CRM automatically communicates conversion data to Google Ads even if you complete transactions physically or over the phone call after a few weeks of follow-up. Automated Bidding will work better for you because your data is constantly updated.
Investigate your campaign’s performance statistics.
Use thorough advertising performance information to ensure you’re investing in your most effective campaigns. When you combine Google Advertisements analytics with CRM revenue data, you can determine which ads and keywords are the most cost-efficient.
Additional resources
Check out these extra resources and use them as recommendations when you build up your Google Ads campaign if you want your Google Ads to generate quality leads and customers.
- Landing Page Best Practices will show you how to create a conversion-optimized landing page, so you don’t squander those valuable clicks.
- Optimized “Thank You” Pages explains what to do with your new lead when they convert, how to keep them on your site, and how to keep their interest.
- Advice for Mobile Google Advertisements teaches you the distinctions between desktop and mobile ads, as well as how to optimize both.
- Optimizing Google Ads Costs will demonstrate how HubSpot maximizes our budget to achieve the highest ROI.
- Quality Google Ads Examples That Convert provides examples of successful Google advertising campaigns.
IMPORTANCE OF GOOGLE ADS
Google Ads, which has mobile and desktop capabilities, is an excellent approach to deliver good-fit traffic to your business by optimizing your products and services in Google; at the same time, ideal consumers are performing comparable searches. With the correct campaign, a company’s internet traffic, phone volume, and in-store visits may all rise.
Businesses may also use the data provided by Google Ads to study and enhance campaigns over time, allowing them to reach more individuals and achieve all of their objectives. Ads may be adjusted to any budget, regardless of the size of the business or available resources, and expenditure can be suspended or discontinued at any moment.
Not only that, but hundreds of businesses use Google Ads to sell their products and services, making it critical for businesses to establish campaigns to stay ahead of their competition. Here are some more advantages of using Google Ads in your company’s digital marketing strategy:
Leads and customers have increased.
Google Ads is one of the most effective channels for generating leads. When your campaigns are properly configured, they may send highly targeted and qualified leads to your website, opt-in form, or other online property. A corporation may also use Google Ads to target clients specifically seeking what they want. This implies that your company’s searches may be regularly adjusted so that only customers interested in purchasing your products or services are sent to your websites via this platform.
Possibility of a High ROI
Unlike other marketing tactics, Google Ads requires advertisers to pay only for advertisements that are clicked on. When your Google Ads campaigns are optimized, you may get a high return on investment (ROI) that you may not have achieved with other tactics. This, however, takes time. To obtain a better image of what would work best for your company, you must constantly test and analyze your campaigns. Google Advertisements is ideal for it offers all of the data needed to calculate ROI and ads clicked keywords entered and cost of clicks.
Learn More About Your Market
Understanding your audience makes dealing with consumers and determining what they want much easier. While this is often tough and time-consuming, Google Ads delivers knowledge on client behaviors and requirements that business owners fantasize about. This includes information on the terms clients use to reach your website, their location, the devices they use, as well as the hours and days of the week they search. You may use this data to improve your products and services or to fine-tune your marketing efforts so that your money isn’t squandered on advertising to those who aren’t interested in your company.
CONCLUSION
Google Ads should be a component of any paid campaign due to its reach and authority. Use the techniques we discussed to get started and remember to tweak and iterate as you go.
There is nothing like a Google Ads campaign that doesn’t work; there are simply those that require a little more attention. You now know everything you need to build a successful Google Ad campaign that drives clicks and converts leads using the above approach and information.


